ALM
Apt-ALM
- Project Name: Apt-ALM (Asset Liability Management)
- Category: Banking
- Start Date: 25-jan-2017
- Status: Complete
- Project Ranking:
5/5
Asset Liability Management
The main objective of Asset Liability Management (ALM) is to effectively hold asset and liability portfolios along the time axis and optimize the RORAC (Return/Risk), using various evaluation and strategy approaches. Due to the complexity of sophisticated mathematical models, effective finance management implies the application of software tools and systems. Our solution accomplishes the following:
- Modeling and pricing of various instrument types.
- Hierarchical structuring of portfolios in assets, liabilities, off-balance positions and their sub-portfolios, using lists, filters and structures.
- Generation and evaluation of cash flows (fixed, float, pay-offs).
- Definition of regular and irregular future periods to be used for ALM analysis.
- Calculation of prices and measures (e.g. Net Present Value) on position level and aggregation on portfolio level.
- Modified duration, convexity, dispersion, internal rate of return, etc..
- Calculation of opportunity rates based on interest rate expressions that can define rates, such as floater, spread, step-up/down, maturity mixed, curve mixed, currency mixed, historical, average, depressed, etc.
- Definition and usage of future scenarios for market factors (FX, interest rates, stock indexes, yield curves, etc.) and for capital development (liquidity scenarios), including prolongation, increase/decrease of business, losses of defaulted debtors, budget plans, future cash flow obligations, etc. The usage of market and liquidity scenarios enables future assessments and stress tests of assets and liabilities. The involvement of simulated positions in the portfolio is a flexible way of planning and investigating future cash flows.
Performance of advanced ALM analysis, related to future interest and capital developments and transformations, including:
- Cash flow analysis and GAP-analysis for future periods, according to cash flow types, such as capital decrease/increase, interest rate payments, expectated pay-offs of stochastically modeled instruments.
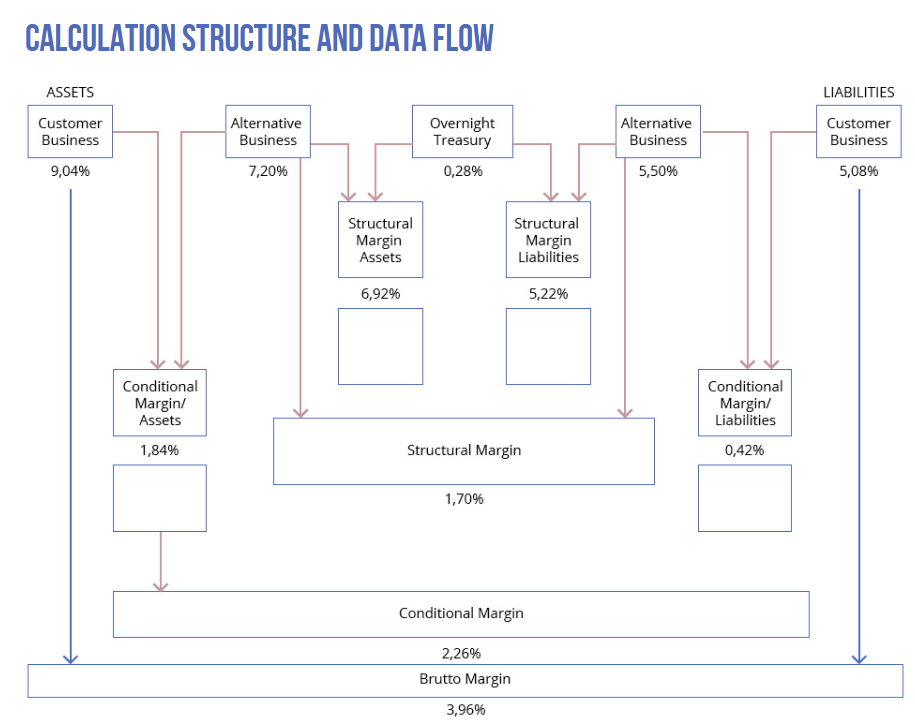
- Interest income analysis that calculates interest rates, margins and contributions for the asset and liability side, based on rates of alternative or market relevant business. Gross, conditional and structural margin and contribution are obtained between the asset and the liability side.
- Fund Transfer Pricing (FTP), that calculates the market value and contributions of assets and liabilities, based on opportunities for alternative businesses with different contract maturities. This functionality is known as maturity transformation, i.e. long-term loans with high interest rates are refinanced by short-term rollover deposits with lower interest rates.
- Refinancing and reinvestment, including the definition of planned positions in order to refinance or reinvest future cash flows.
- Replication of portfolios, used to model future financial instruments without knowing the cash flows or pay-offs, such as rollovers and non-term liabilities.